Renewable energy, new energy
In order to solve this contradiction, there are two ways, usually the priority is to ensure the selectivity of the action, that is, to ensure that the next line exit is not activated when the protection device startup parameter is set. In the microcomputer protection technology, this is also called To avoid the short-circuit condition setting at the exit of the next line, another method is to use an automatic reclosing to correct this non-selective action in the individual case when the quick-cut fault is the primary condition.
When the electrical equipment in the power grid fails, the short-circuit current is very large. According to the basic operating principle of the relay, if the short-circuit current is determined as the operating current of the relay by calculation in advance, the faulty device can be protected. Overcurrent protection and current quick-break protection are based on this principle. In order to ensure the selectivity of the action, according to the characteristics of the short-circuit current (the closer the fault point is to the power supply, the larger the short-circuit current), the overcurrent protection has an action time limit, and the current quick-break protection has no action time limit, that is, when a short circuit occurs. When it immediately moves to cut off the fault, it has no time limit characteristics and is often used in conjunction with overcurrent protection.
The quick-break protection cannot protect the full length of the line, only selectively protects part of the line, and the remaining part is the dead zone of quick-break protection. In order to avoid the above situation, the quick-break protection can also be made into a slight time limit, which is called time-limited current quick-break protection. It cooperates with the untimed current to eliminate the action dead zone of the current quick-break protection.
Related articles
-
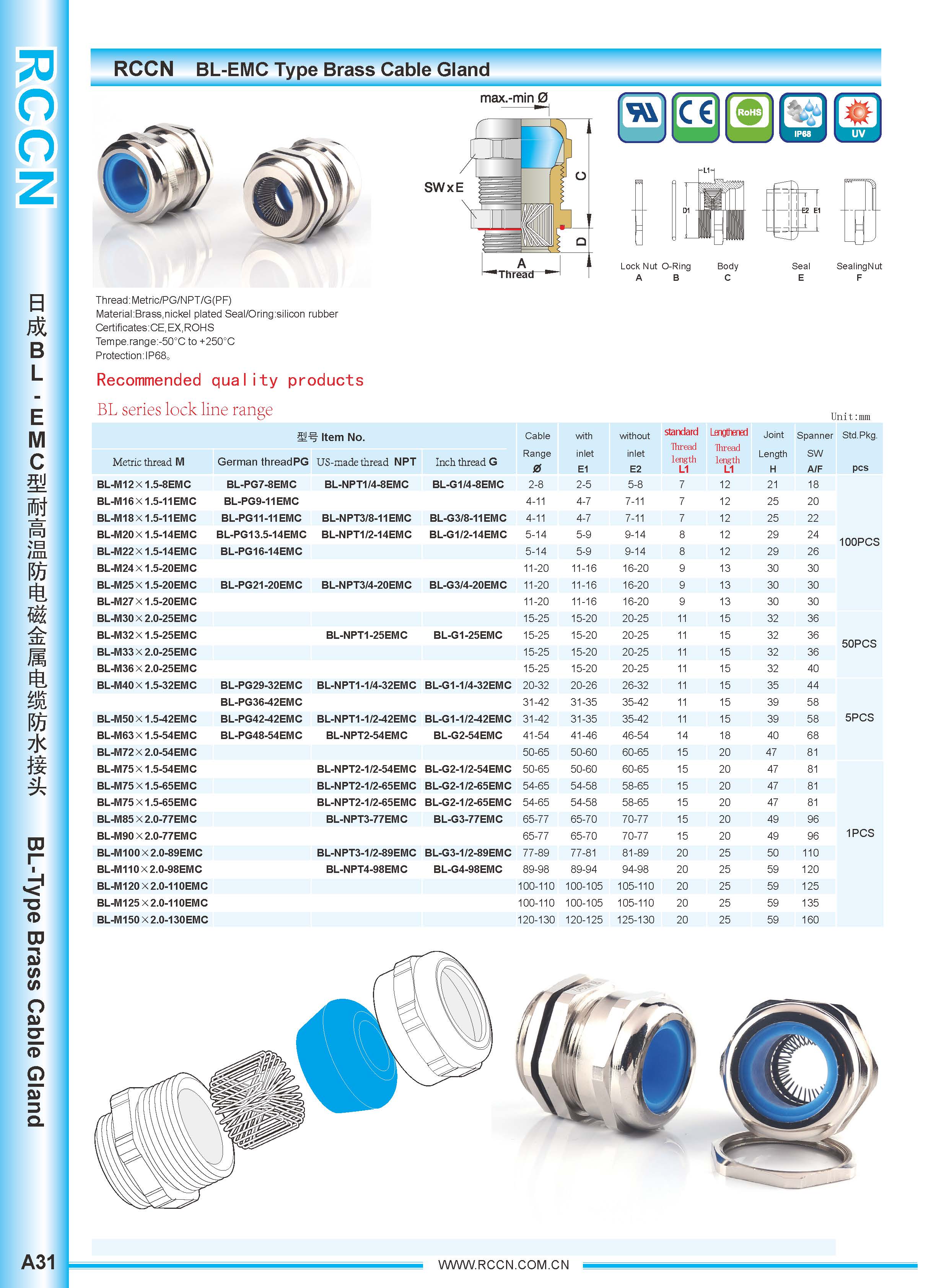
BL-EM anti-electromagnetic metal cable connector IP68
BL-EM anti-electromagnetic metal cable connector IP68
-
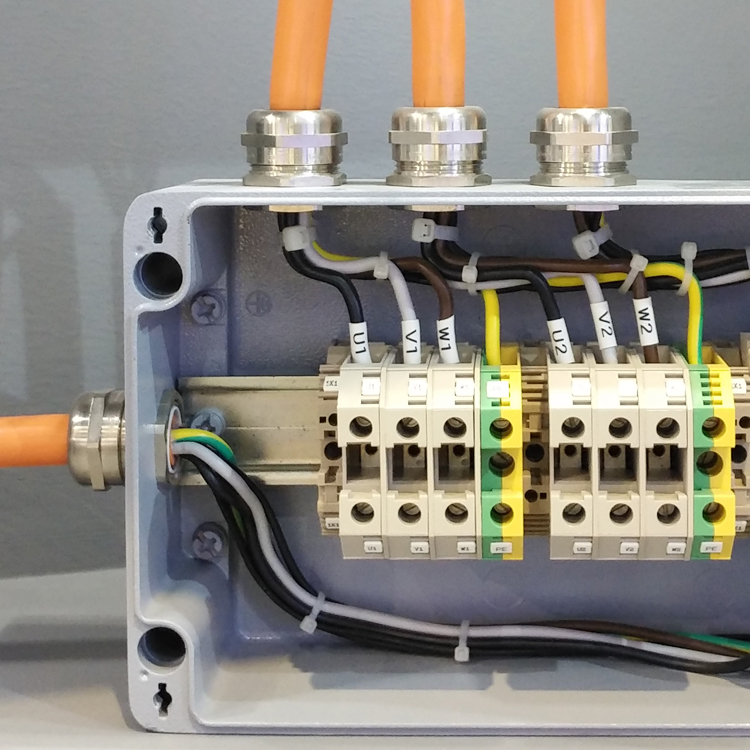
Metal cable connector in the motor installation effect diagram
Metal cable connector in the motor installation effect diagram
-

Metal cable connectors need to be properly installed and used
Cable connectors are the most common type of device at this stage. They are divided into different categories. We can see the most common metal joints, waterproof joints, etc. Although such a cable co
-

Metal cable connectors need to be properly installed and used
Cable connectors are the most common type of device at this stage. They are divided into different categories. We can see the most common metal joints, waterproof joints, etc. Although such a cable co
-

Cable joint material and performance
The cable connector is mainly used to connect the connector equipment between the two disconnected cables. The overall connection is good and has a certain tightness. Therefore, during use, leakage wi
-
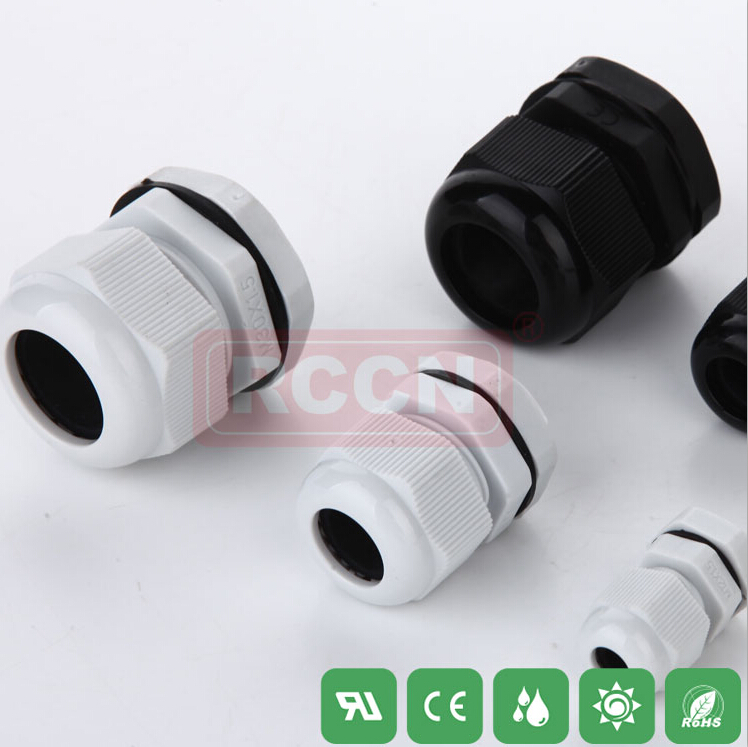

Cable waterproof connector selection guide
As the name suggests, cable waterproof connectors can be applied to water-borne environments to provide a safe and reliable connector connector, the most important of which is the ability to achieve w
-
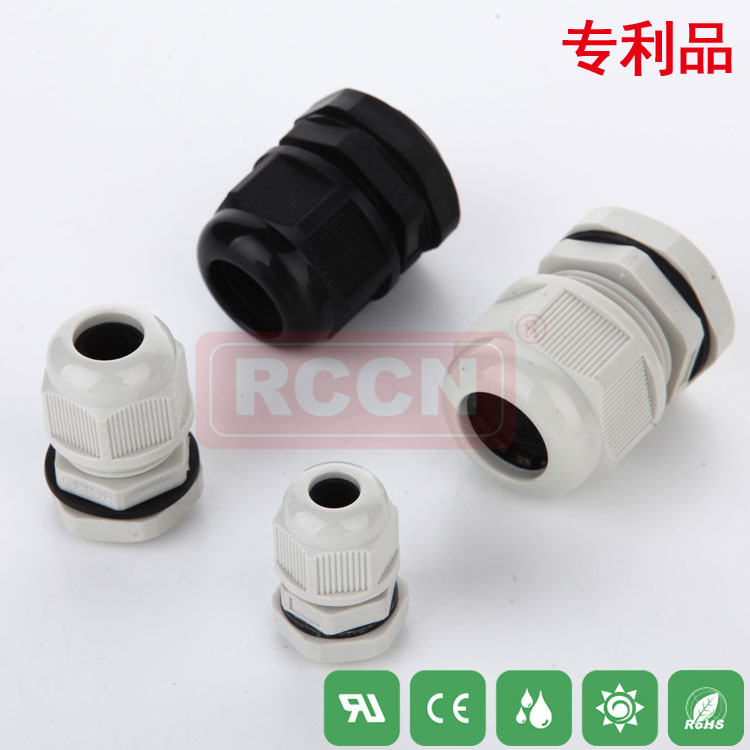

Cable joint fire protection method
The high-voltage cable joint fire protection method comprises the following steps: an explosion-proof temperature and humidity sensor detects the temperature and humidity in the fire protection box, a
-
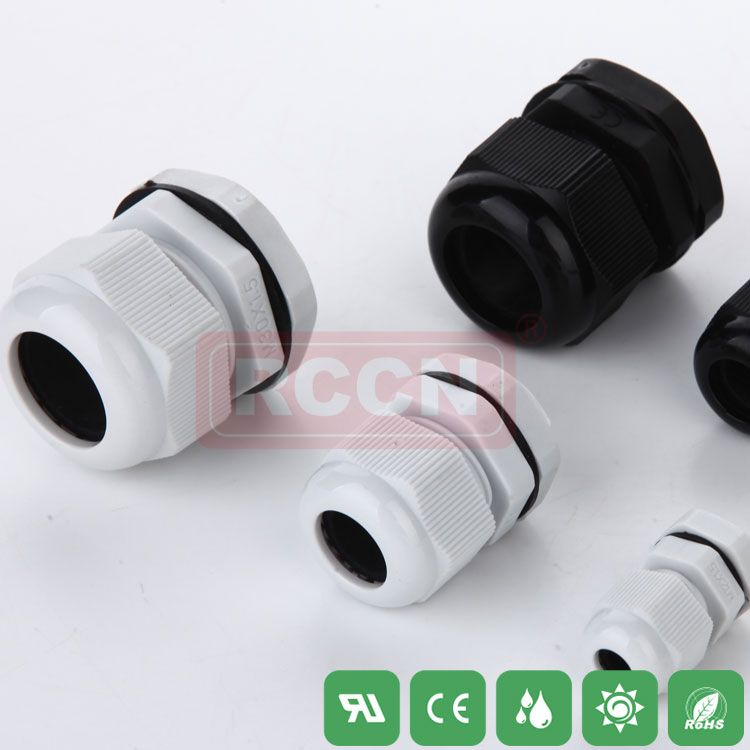

How to prevent the cable waterproof joint from breaking?
In the prior art, the cable reciprocates for a long period of time, and the sheath layer is often worn. In the electrical equipment and cable connection portion, the reciprocating motion of the outlet












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite