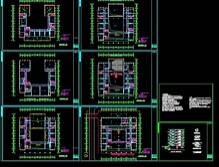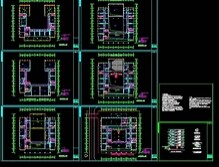
Electrical diagram
A graphical representation of the interrelationships and connections of components in an electrical system or device by means of electrical graphic symbols, annotated enclosures, or simplified profiles. A curve that indicates the relationship between two or more variables in a broad sense to describe the interrelationships or connections of components in a system, plant, or plant, or tables, text, etc. used to provide operating parameters. Electrical diagram of the column.
one,
Electrical diagram classification
1, system diagram or block diagram: with symbols or annotated box, a rough representation of the basic components of the system or subsystem, the relationship between the main features and a simple diagram.
2, the circuit diagram: Graphic symbols and work order, the details of the circuit, equipment or complete set of all the components and connections, regardless of their actual location of a diagram. The purpose is to facilitate a detailed understanding of the principle of action, analysis and calculation of circuit characteristics.
3, function diagram: that the theory or the ideal circuit without involving a method of implementation of a map, its purpose is to provide a drawing circuit or other basis for the relevant diagram.
4, the logic diagram: the main binary logic (and, or, or XOR, etc.) drawing a simple graphical symbols, which only show that the function does not involve the implementation of the logic diagram called pure logic diagram.
5, function chart: that the role of the control system and a state diagram.
6, equivalent circuit diagram: that the theory or ideal components (such as R, L, C) and a connection between the functional diagram.
7, the program diagram: a detailed representation of program elements and program pieces and a diagram of the interconnection relationship.
8, equipment components table: the complete sets of equipment, equipment and devices in the various components and the corresponding data in the form of its use that the components of the name, model, specifications and quantity.
9, the terminal function diagram: that all functional units external terminal, and use the function diagram, table diagram or text that a schematic diagram of its internal functions.
10, wiring diagram or wiring table: that sets of equipment, equipment or device connection, wiring and inspection for a diagram or table.
(1) unit wiring diagram or unit wiring table: that sets of equipment or equipment in a structural unit within the connection relationship between a wiring diagram or wiring table. (A structural unit refers to a component or a combination of components that can operate independently in each case)
⑵ interconnect wiring diagram or interconnect wiring table: that sets of equipment or equipment, the connection between the different units of a connection or wiring table. (Cable wiring diagram or wiring table)
(3) Terminal Wiring Diagram or Terminal Wiring Table: A wiring diagram or wiring table indicating the terminals of the unit or equipment, and the external wiring (if necessary, including internal wiring) connected to the terminals.
⑷ tariff configuration table or electricity configuration table: to provide both ends of the cable position, if necessary, including electricity functions, features and path information such as a wiring diagram or wiring table.
11, data sheet: the specific items given detailed information on the information.
A schematic diagram or location diagram showing the location of items in a plant, plant, or plant. Refers to the use of graphical symbols to draw the map, used to indicate a region or a building within the electrical components of the location and connection wiring.
two,
Electrical characteristics of the map
1, the role of electrical diagram: explain the working principle of electricity, describe the composition and function of products, installation and use of information to provide an important tool and means.
2, the schematic diagram is the main expression of the electrical diagram is to use graphic symbols, annotated enclosure or simplified outline that the system or equipment components and the relationship between the relationship between a diagram.
3, components and connectors is the electrical diagram of the main expression
⑴ a circuit usually by the power supply, switching equipment, electrical equipment and connecting line of four parts, if the power equipment, switching equipment and electrical equipment as components, the circuit consists of components and cables, or a variety of components In accordance with a certain order with the connection line up to form a circuit.
⑵ components and connection lines that way
① components for the circuit diagram when there is a centralized representation, separate representation, semi-centralized representation.
② components for the layout of the map when the location of the layout and function of the layout method.
③ connection line for the circuit when the single-line representation and multi-line representation.
④ connection line for wiring diagram and other drawings when the continuous line representation and interrupt line representation.
4, graphic symbols, text symbols (or project code) is the electrical diagram of the main components. An electrical system or an electrical device is made up of a variety of components. In the electrical diagram, which is expressed mainly in the form of a diagram, it is usually represented by a simple graphical symbol, whether it is a representation, a function, or an electrical connection.
5, the energy flow, information flow, logic flow, functional flow of the different description of the diversity of the electrical diagram. An electrical system, a variety of electrical equipment and devices, from different angles, different side there are different relationships.
⑴ energy flow - the flow of energy and transmission.
⑵ information flow - the flow of signals and transmission.
Logic flow - the logical relationship between each other.
⑷ functional flow - the functional relationship between each other.
three,
Graphical symbols for electrical diagrams
1, the meaning of graphic symbols: used for drawings or other documents to represent a device or concept of graphics, tags or characters. Or graphic symbol is a visual graphic produced by writing, drawing, printing, or other means, a means of conveying information in a concise manner, representing a physical or concept, and providing information about conditions, correlations, and actions Information of the industrial language.
2, graphic symbols from the general symbols, symbol elements, symbols and other components.
⑴, the general symbol: that a class of products or such products, a usually very simple symbols.
⑵, symbol elements: it has a definite meaning of simple graphics, must be combined with other graphics to form a device or a complete symbol of the concept.
(3), the definition of symbols: to provide additional information on the addition of a symbol on the other symbols. It can not be used alone, but general symbols are sometimes used as qualifying symbols.
Type of qualified symbols:
①, the current and voltage types: such as AC, DC, AC frequency range, DC positive, negative, neutral, neutral and so on.
②, variability: variability is divided into intrinsic and non-intrinsic.
The intrinsic variability refers to the variable depending on the nature of the device itself, such as varistor resistance with voltage changes.
Non-intrinsic variability means that the variable is controlled by external devices, such as the resistance of the slip-wire resistor is adjusted by external means.
③, force and movement direction: with solid arrow symbols that force and movement direction.
④, flow direction: open arrow symbol with the energy, signal flow direction.
⑤, the characteristic amount of the action relevance: it refers to the device, components and sketches or normal values such as compared to the action characteristics, the usual definition of the symbol is>, <, =, ≈ and so on. ⑥, material type: available chemical element symbols or graphics as qualified symbols.
⑦, effects or relevance: refers to the thermal effect, electromagnetic effect, magnetostrictive effect, magnetic field effect, delay and delay. Respectively, with different symbols added to the general symbols on the components that are added symbols of the functions and characteristics. The use of qualified symbols makes the graphical symbols more versatile.
⑷, box symbol: that components, devices and other combinations and their functions, not to give the details of the device, the device does not take into account all the connections of a simple graphical symbols.
3, the classification of graphic symbols
⑴, wire and connecting devices: a variety of wires, wiring terminals and wire connections, connecting devices, cable accessories.
⑵, passive components: including resistors, capacitors, inductors and so on.
⑶ semiconductor tubes and tubes: including diodes, transistors, thyristors, tubes, radiation detectors.
⑷ the occurrence and conversion of electrical energy: including windings, generators, motors, transformers, converters and so on.
⑸ switches, control and protection devices: including contacts (contacts), switches, switchgear, control devices, motor starters, relays, fuses, gaps, arrester and so on.
⑹ measuring instruments, lights and signal devices: including the instructions integrated and recording instruments, thermocouples, telemetry devices, clocks, sensors, lights, speakers and bells and so on.
⑺ telecommunications switching and peripherals: including switching systems, selectors, telephones, telegraph and data processing equipment, fax machines, transducers, recording and playback.
⑻ telecommunications transmission: including communication circuits, antennas, wireless stations and a variety of telecommunications transmission equipment.
⑼ power, lighting and telecommunications arrangements: including power plants, substations, networks, audio and television cable distribution system, switches, sockets pinout, lamp leads, installation symbols. Applies to electrical, lighting and telecommunications systems and floor plans.
⑽ binary logic unit: including the combination and timing unit, the unit operator, delay unit, bistable, monostable and unstable units, displacement registers, counters and storage and so on.
⑾ simulation unit: including the function, coordinate converter, electronic switches
4, commonly used graphical symbols of the application
⑴, all the graphical symbols, by no voltage, no external force of the normal state of the show.
⑵, in the graphical symbols, some of the device elements have multiple graphical symbols, there are preferred forms, other forms, form 1, form 2 and so on. The principle of choosing symbols is as follows: use the optimal form as far as possible; use the simplest form as far as possible when the need is satisfied; use the same form in the figure of the same figure.
(3) The size of the symbols and the width of the graphs generally do not affect the meaning of the symbols. In some cases, symbols of different sizes and different widths are permitted in order to emphasize certain aspects or to facilitate the supplemental information or to distinguish between different uses Figure line.
⑷, in order to maintain a clear picture, to avoid bending or crossing the wire, without causing misunderstanding in the case, the symbol can be rotated or placed into a mirror, but at this time graphic symbols marked and the direction of the text can not be reversed.
⑸, graphics symbols are generally drawn with lead, but in most cases the location of the lead wire is only used as an example, without changing the meaning of symbols under the principle of lead in different directions. Such as the location of lead symbols affect the meaning of symbols, you can not arbitrarily change, or cause ambiguity.
⑹, GB4728 in a relatively complete list of ugly symbolic elements, limited symbols and general symbols, but the combination of symbols is limited. If the graphical symbols of some particular device or concept are not listed in the standard, new symbols may be derived from the combination of the specified generic symbols, qualifying symbols and symbolic elements.
⑺, symbol drawing: electrical diagram with graphical symbols are drawn out by the grid, but the grid is not shown with the symbol.
four,
Graphical symbols for use in electrical equipment
1, electrical equipment, graphic symbols are completely different from the electrical diagram with a symbol of another symbol. It is mainly applicable to all kinds of electrical equipment or electrical equipment components, so that the use of its operators and methods of operation can also be used to install or move electrical equipment occasions, such as prohibitions, warnings, regulations or restrictions on matters of note.
2, electrical equipment, the use of graphical symbols: identification, qualification, instructions, orders, warnings, instructions.
3, equipment, graphic symbols must be drawn in proportion. Clear meaning, simple graphics, clear, easy to understand, easy to identify and identify.
Fives,
ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY Chinese characters
1, electrical technology in the text symbols in the basic text symbols and auxiliary text symbols. Basic text symbols are divided into single-letter symbols and two-letter symbols.
2, single-letter symbols: the Latin alphabet will be a variety of electrical equipment, devices and components are divided into 23 categories, each category with a dedicated one-letter symbols. Such as R for the resistor, Q for the power circuit switching devices and so on.
3, two-letter symbols: that type of single letter and another letter, the combination of type to single-letter symbols in front of another letter listed in the order after. Another letter in a two-letter symbol usually uses the first letter of the English term for a device, device, or component, or a common abbreviation, or conventionally used letters.
4, auxiliary text symbols: that electrical equipment, devices and components, and line functions, status and sacrifices, usually by the English word before the first two letters. It is generally placed behind the basic text symbols, constitute a combination of text symbols.
5, supplement the principle of text symbols:
⑴, without prejudice to the principles described above, based on the international standards can be used in electrical technical symbols.
(2) The two-letter symbols and the auxiliary characters are supplemented with the priority given to the single-letter, two-letter and auxiliary characters.
⑶, text symbols should be in accordance with the relevant national terminology of electrical terms or professional standards in the English terms abbreviated form. If there are several names of the same device, you should use one of the names. When the device name, function, status or characteristics of an English word, the general use of the first letter of the words constitute text symbols, if necessary, the first two letters can be used, or the first two syllables of the first letter, or the use of common reduction When the equipment name, function, state or sacrifice for the two or three English words, the general use of the two or three audio first letter, or the use of commonly used abbreviations or conventionally used The idiomatic form constitutes a literal symbol.
⑷, because I, O easy to be confused with 1 and 0, therefore, not allowed as a separate text symbols.
six,
Project code in electrical technology
1, the project code: to identify the map, table map, table and equipment on the types of projects, and provide the project hierarchy, the actual location of a specific code information.
2, access to the project code can be a different map or other technical documents on the project (software) and the actual equipment in the project (hardware) one to one correspondence and together.
3, the project code from the Latin alphabet, Arabic numerals, a specific prefix symbols, in accordance with certain rules combined code. A complete project code contains four code segments:
High-level code segment, the prefix symbol "=";
Type code section, the prefix symbol "-";
Location code section, the prefix symbol "+";
Terminal code section, the prefix symbol is ":".
4, type code: to identify the type of project code. There are three representations
⑴, by the letter code and numbers.
-K2
Category Code Section Prefix Symbol + Item Type Alphabet code + Number of the same item category
-K2M
Prefix symbol + alphabetic code of category + serial number of the same item type + function letter of the item Code
2, with the sequence number (1, 2, 3, ...) that the various items in the figure, while the sequence number and the items it represents in the figure or other description, such as -1, -2, -3 ...
⑶, for different types of projects using different groups of numbers. Such as for current relays 11, 12, 13, ....
Such as the use of separate representation of the relay, can be added after the number "."
5, high-level code refers to the system or equipment at any higher level (for the code item) project code. For example, the switch Q3 in the S2 system is represented by = S2-Q3, where = S2 is the upper-level code.
6, location code refers to the item in the component, equipment, system or building the actual location of the code. The location code consists of the Latin letters or numbers specified. When a position code is used, a schematic representation of the position of the item is given. Such as + 204 + A + 4 can be written as + 204A4, meaning A column cabinet installed in Room 204, No. 4 cabinet.
7, the terminal code is usually not combined with the first three paragraphs, only with the type code combination. Can be used in digital or capital letters, -S4: A said control switch S4 of the A number of terminals, an XT: 7 that the terminal board XT No. 7 terminal.
8, the application of the project code:
= High-level code segment - type code segment (space) + position code segment
Wherein the high-level code segment is a functional subordination relation to the type code segment, and the position code segment is position information for the type code segment.
Such as = A1-K1 + C8S1M4 A1 relay that the device K1, the location of the control cabinet in the C8 interval S1 cabinet M4;
= A1P2-Q4K2 + C1S3M6 represents the relay K2 in the Q4 switch of the A1 unit P2 system and is located in the C1 range of the operating cabinet M6 in the C1 range.
Seven,
General rules for electrical diagrams
1, the electrical diagram of the composition: border line, frame line, title bar, sign column composition.
2, size and size: the border line into the picture
⑴, format size divided into five categories: A0-A4 in Table 1
A0-A2, drawings in general may not be lengthened.
A3, A4 drawings, according to the need, along the short side lengthened.
⑵, select the size of the basic premise: to ensure that the layout of compact, clear and easy to use.
⑶, format selection considerations: ①, the design of the object size and complexity.
②, the level of detail determined by the type of diagram.
③, try to use a smaller format.
④, to facilitate the binding and management of drawings.
⑤, copy and micro-requirements.
⑥, computer-aided design requirements.
3, the title bar is used to determine the design name, drawing number, Zhang times, changes and the contents of the signature of the column, the equivalent of the design "nameplate."
The location of the title bar is usually in the bottom right or bottom of the drawing. The direction of the text in the title bar is the direction of the picture, and the sign bar is used for the signature and date of the design of the relevant professional designers.
4, the pattern number and the accession number by the drawing of two parts.
5, the map of the distinction: in the figure of the border, the vertical direction with capital letters Latin alphabet, transverse direction with Arabic numerals, numbered from the title bar relative to the upper left corner, partition number is even. Area code for the letters + numbers.
As in the same figure No. 34 A6 area, marked 34 / A6;
Figure 3219 single figure F3 area, marked as: Figure 3219 / F3;
Figure 28 is shown in Figure 28, area G8, labeled 4752/28 / G8;
In the = S2 system single image C2 area marked as S2 / C2;
In the area of Figure 31 of Figure 31, labeled SP = SP1 / E7
Plus the size of the dots
title
Pattern number - drawing number and search number
Fonts
Eight,
Graph lines, fonts and others
A, B, C, D, F, G, dashed line, dotted line, dotted line, thick dotted line, double dotted line, J, K.
2, font: as shown above
3, arrows and guidelines
Open Arrow: for electrical energy, electrical signal transmission direction (energy flow, information flow direction)
Solid arrow: Used for variability, force or direction of motion, and direction of the leader line.
Guideline: The object that indicates the annotation should be a thin solid line.
Point the end of the leader line Mark: Point to the contour line, with a black dot; point to the contour line, with a solid arrow; point to the electrical connection line plus a dash.
4, Wai box: When you need to display a part of the graph, such as functional units, structural units, the project group, the available dotted line enclosure. If the figure contains the function installed in other parts and the figure related to this part of the two-dotted line can be added.
5, the ratio: the size of the graphics on the map size and physical size ratio. Generally used to reduce the proportion of series: 1: 10,1: 20,1: 50,1: 100,1: 200,1: 500.
6, size injection method
The dimension consists of four dimensions: dimension line, dimension line, dimension start and stop arrow (or 45º dash), and dimension number.
⑴, the size of the basic rules of note
①, the true size of the object should be based on the size of the figures on the drawings, and graphic size and drawing accuracy has nothing to do.
②, the figure in the size of the figures, if not clearly stated, all in mm units.
③, the size of the marked in the drawings, the drawings for the final size of the mechanical parts.
④, the object of each size, generally only marked once, and should be marked in the structure of the most clear reflection of the graphics.
⑵, size injection method
①, linear size (length, width, thickness) of the size of the number of general note above the size of the line can also be written in the size of the line break.
②, the angle of the number of horizontal all written in the direction, note the line in the size of the interruption, can also lead to write the way.
③, in the absence of sufficient position to draw arrows or note the figures can also remove the label.
④, some specific size must be marked with symbols, such as the diameter of the symbol Φ, radius of the symbol R, the ball symbol S, spherical diameter symbol SΦ, spherical radius of the symbol SR, the thickness of the symbol δ, with the reference size with (). Square symbols with □.
7, the installation of elevation with absolute elevation and relative elevation of the points.
Absolute elevation: altitude altitude in Qingdao City, the Yellow Sea plane as a zero and determine the height of the size.
Relative Elevation: The height dimension that is selected when a reference plane or reference point is zero.
Electrical location maps are used relative elevation, the general use of a certain outdoor plane, a floor plane as a zero and calculate the height. This elevation is called the installation elevation or laying elevation.
8, the location: electrical lighting and telecommunications layout maps and other types of drawings according to the north and south, the right east and left the electrical equipment or structure that the location and orientation, but in many cases need to use the orientation of its orientation.
Wind direction frequency mark: that the installation of regional wind direction of the situation throughout the year, the electrical layout diagram is also often marked with the frequency of the wind direction. It is based on this area for many years the average number of times in all directions the percentage of hair, drawn by a certain percentage.
9, the building location axis: where the load-bearing walls, columns, beams and other major load-bearing components of the location of the painted axis.
The basic principle of positioning the axis number: in the horizontal direction, from left to right with the order of the Arabic numerals; vertical direction, with the Latin alphabet from bottom to top preparation; numbers and letters with dash.
nine,
The layout of the diagram
1, mechanical drawing and schematic diagram of the difference between the layout method: mechanical drawings must be strictly according to the location of the layout of the parts, and the layout of the diagram can be flexible according to specific circumstances.
2, the layout of the graph: that wire, signal path, connection lines and other lines should generally be a straight line, that is horizontal and vertical, as far as possible to reduce the cross and bending.
⑴, horizontal layout: the equipment and components arranged by row, so that its cable is generally arranged horizontally.
⑵, vertical layout: the equipment or components arranged in columns, connecting lines into a vertical arrangement.
⑶, cross-layout: the corresponding components connected into a symmetrical layout.
3, the layout of the circuit or components
⑴, functional layout method: schematic symbols in the arrangement, only to facilitate that they can be seen that the functional relationship between the components, regardless of the actual location of a layout method. In this layout, the representation object is divided into functional groups arranged from left to right or from top to bottom in causality, and the elements of each functional group are arranged together in the order of work, as far as possible. Most electrical diagrams are functional diagrams. Layout to comply with the principle:
①, the layout order should be from left to right or from top to bottom.
②, if the information flow or energy flow from right to left or from top to bottom, and the flow is not obvious to the picture, the connection should be drawn on the opening arrow. Open arrows should not be adjacent to other symbols.
③, in a closed circuit, the flow of information on the forward path should be from left to right or from top to bottom. The direction of the feedback path is opposite.
④, drawing the introduction of the best draw lines drawn in the drawing near the border.
⑵, location layout method: refers to the schematic symbols in the arrangement of symbols corresponding to the actual location of the component layout. This layout shows the relative position of the components and the orientation of the wires.
ten,
Basic Representation of Electrical Diagrams
Multi-line representation of the circuit and single-line representation
1, multi-line representation: each cable or wire each with a line that the method.
Features: can be expressed in detail the contents of each phase or line, especially in each phase or line content asymmetry of the case using this method.
2, single-line representation: two or more than two connection lines or wires, only a line method.
Features: For three-phase or multi-line basic symmetry of the situation.
3, mixed representation: part of a single line, part of the multi-line.
Features: both simple single-line representation of the characteristics of refining, but also both multi-line representation of the object to describe the precise and sufficient advantages, and because the two co-exist, change, and flexible.
Eleven, the electrical components of the centralized representation and separate representation
1, centralized representation: the device or a set of components in a project of the graphical symbols in the diagram on the method of drawing together.
Scope and characteristics: a simple diagram. The components are connected to each other by a mechanical connecting line (broken line). The cable must be straight.
2, semi-concentrated representation: In order to make the device and device circuit layout is clear, easy to identify, a project in some parts of the graphical symbols, arranged separately on the diagram, and mechanical connection symbols that the relationship between them.
Mechanical connections can be bent, branched and crossed.
3, separate representation: In order to make the device and device layout of the circuit clear and easy to identify, to a project in some parts of the graphical symbols, arranged separately on the diagram, and only use the project code to represent the relationship between them.
Separate representations are given the same amount of information as the graphs using a centralized or semi-centralized representation.
4, the three methods are shown in Figure
5, the project code of the labeling method
(1), the use of concentrated and semi-centralized representation of the components drawn, the project code is only marked once in the symbol and aligned with the mechanical connection line.
⑵, the use of separate representation of the components drawn, the project code should be in each part of the project symbol next to the mark.
(3), the project code should be placed as close to the top of the graphic symbol, especially the third paragraph of the project code (type code) is close to the center of the symbol.
⑷, when the circuit is arranged horizontally, the item code is marked above the symbol, when the circuit is arranged vertically, the item code is marked on the left side of the symbol. The item code is written horizontally, top to bottom or left to right.
⑸, the project code in the terminal code is marked on the terminal or terminal position next to.
⑹, for the painted box with a box of functional units and structural units, the project code on the box marked on the top or left.
⑺, in most cases, the high-level code in the project code can be marked in the title bar or the top of the drawing to simplify the symbol next to the label of the project code.
twelve.
Electrical components, contact position, work status and technical data representation
1, contacts are divided into two categories: a class by electromagnetic force or manual operation of the contacts (contactors, electrical relays, switches, buttons, etc.); the other for non-electric and non-manual contact (non-electrical relays, Stroke switches, etc.).
2, the contact: ① contactors, electrical relays, switches, buttons and other items of the contact symbol in the same circuit, the power and the force, the contact symbol of the action direction should be consistent, when the contact This is especially true in the case of hold, latch and delay functions.
②, non-electric and non-manual operation of the contact must be in the vicinity of its contact symbol indicates the mode of operation. They are represented by graphics, operating device symbols, and comments, tags, and tables.
3, the working state of the component representation: components, devices and equipment, the movable part should normally be expressed in the non-excited or not working state or position.
⑴, relays and contactors in the non-excited state;
⑵, circuit breakers, load switches and disconnectors in the off position;
⑶, with a zero position of the manual control switch in the zero position, without manual control switch zero position in the figure specified position;
⑷, the mechanical operation of the operating state of the switch and work position of the corresponding relationship should generally be expressed in the vicinity of its contact symbol, or with instructions.
Accidents, standby, alarm and other switches should be said that the normal use of equipment in the position of the various components of the multi-opening and closing devices must be expressed in a position consistent with each other, regardless of the working state of the circuit.
4, the components of the technical data of the labeling method: electrical components of technical data generally marked in the vicinity of the graphical symbols. When the connection lines are arranged horizontally, they are marked as far as possible below the graphic symbols. When they are arranged vertically, they are marked below the item codes. They can also be marked in the box symbols or simplified outline symbols.
5, the annotations and signs that the method
⑴, annotation of the two methods: directly to the object to be described in the vicinity of the map and the Notes on the other location.
⑵, if there is information on the device panel signs, you should be related to the graphical symbols of components with the same logo.
13. Representation of component terminals
1, the terminal: in the electrical components, to connect the external conductive wire components.
Terminal classification: fixed terminal and removable terminal.
Fixed terminal graphic symbol: 0 or ·;
Removable terminal graphic symbols: Φ
2, to alphanumeric symbols mark the principles and methods of terminals
(1), the two components of a single endpoint with two consecutive numbers. The individual terminals in the middle of the individual elements are represented by numerals with natural increasing numbers.
⑵, the same component group
①, preceded by letters in letters, such as signs of three-phase AC system letters U1, V1, W1 and so on.
②, if you do not need to distinguish between different, the available number 1.1,2.1,3.1 signs.
⑶, the same group of components
⑷ connected with a specific wire electrical terminal signs. See the following table and figure.
3, the terminal code of the labeling method
(1) The terminal designation for resistors, relays, analog and digital hardware shall be marked on the outside of the outline of its graphical symbol. The function and annotation of the part are marked in the symbol outline.
⑵, for the field connection, test and fault detection of the connection device should be marked for each connection point terminal code.
(3) In the functional unit or structure unit with the frame, the terminal code must be marked in the box to avoid being misunderstood.
14, cable: In the electrical diagram, a variety of graphical symbols of the mutual connection.
1, the wire representation
2, the thickness of the graph: power main circuit, a circuit, the main signal path using thick lines, with the rest of the thin line.
3, the cable group: bus, bus, distribution harness, multi-core wire and cable can be regarded as parallel cable. For multiple parallel connection lines, they should be grouped according to their functions, and can not be grouped in near functions. They can be grouped in groups of no more than three. Group spacing is greater than the distance between lines.
Connection Marking: Marking is usually placed above the connection line, can also be placed in the interruption of the connection line, if necessary, can also be marked on the connection signal characteristics of the information.
4, the wire connection point that method
⑴, T-shaped connection point can be added solid dot (·);
⑵, + -shaped connection point can be added solid dot (·);
3, on the cross but not connected to the two lines, in the intersection can not add solid dots, and should avoid changing the direction at the cross, but also to avoid the connection through the other connection points.
15, continuous connection cable representation and interrupt representation
1, with a single line that the continuous line of representation
2, the cable interrupt representation
⑴, through the picture of the connection line is longer or through the dense area, allowing the interruption of the connection line, in the interruption of the corresponding mark.
(2), to the same line group can be said that the interrupt line, and interrupt both ends were marked with the appropriate mark.
(3), a graph need to be connected to another map up, you must use the interrupt line
⑷, with symbolic mark that the interruption of the cable.
16, the identification of wire marking and labeling methods
1, the identification of wire mark: marked on both ends of the wire or wire harness, if necessary, marked in the full length of the visible parts (or marked on the graph) to identify the wire or harness markings.
2, the main mark: marking only the characteristics of wire or wire harness, regardless of its electrical function of the marking system. The main tag is divided into subordinate tag, independent tag and combination tag.
3, the subordinate mark: the wire connected to the terminal mark or wiring harness connected to the device based on the marking wire or wire harness marking system. Subordinate tags are subordinate to local tag, slave remote tag, and subordinate tag. ⑴, subordinate to the end of the mark: wire or wire harness terminal mark and its connected terminals or equipment components of the marking system.
⑵, subordinate far-end mark: wire or wiring harness terminal marked with the remote terminal connected to the device or the same part of the marking system.
⑶, subordinate both ends of the mark: the end of each wire or wire harness marked with the local terminal tag connected with the remote tag or the end of the device components of the marking system.
Example of an interrupt line slave tag
4, the independent mark: the wire connected to the terminal mark or wiring harness connected to the device regardless of the mark or wire harness marking system. The two wires are marked with 1 and 2, respectively, and are not related to the terminal marks at both ends. This marking method is only used in the electrical wiring diagram represented by the continuous wire method.
5, the combination of tags: subordinate tag and independent tag used in conjunction with the marking system. Subordinate local mark and combination mark used together with the independent mark, two wires are marked as A1-1-Ba \ A3-2-Bd.
6, supplementary mark: It is generally used as the main mark of the supplement, and to each wire or wire harness electrical function as the basis. Supplementary markings are usually indicated by letters or specific symbols. To avoid confusion, the supplementary markings and the primary markings are separated by a symbol.
Seventeen, system diagram and block diagram of the basic features and uses
1, the system diagram and block diagram: with symbols or annotated box, outline the basic components of the system or subsystem, the relationship between the main features and a simple diagram.
2, the system diagram and block diagram in common: are marked with a symbol or to indicate the box.
System diagram is usually used to represent a system or a set of devices, and block diagram is usually used to represent subsystems or equipment; system diagram if the annotation of the project code, usually high-level code, block diagram if the annotation of the project code, usually category code.
3, the role of the electrical system diagram and block diagram:
⑴, as a basis for further preparation of detailed technical documents.
⑵, for operation and maintenance reference.
⑶, for the relevant departments to understand the design of the overall program, a brief working principle and the main composition of the profile.
Eighteen, system diagram and block diagram of the basic principles and methods of drawing
1, the use of graphic symbols
⑴, the use of box symbols: box symbols that components, devices and other combinations and their functions, not given components, equipment details, and not consider all the connections of a simple graphical symbols.
(2), with annotated box: the system diagram and block diagram of the box may be a system, subsystems, complete sets of equipment or functional units, with annotated box to represent the object. Box in the form of a solid line box and dotted line box, dotted line box contains a large capacity, see Figure.
2, the level of division: a higher level system diagram and block diagram can reflect the object profile; lower level system diagram and block diagram, the object can be expressed in more detail.
3, the project code of the labeling method
⑴, in the system diagram and block diagram, the box marked on the project code.
(2) the higher level of the system diagram marked on the high-level code; the lower level of the block diagram, marked type code.
⑶, the system diagram and block diagram does not specify the actual project line and installation location, it is generally not marked with the terminal code and location code.
⑷, the project code is marked in the box above or above the left.
4, the connection line that way
⑴ connection method: When drawing with a dotted line drawing, the connection line connected to the box on the graphical symbols, when the use of box symbols or annotated solid line box, the connection line connected to the outline of the box on.
⑵, cable type: wire connection - thin solid line
Power supply circuit and the main signal circuit - thick solid line
Mechanical connection - dashed line
⑶, signal flow: the system diagram and block diagram of the layout, clear and conducive to the identification process and the flow of information. The flow of control signals is plotted perpendicular to the process flow, with the open arrows indicating electrical signal flow and the solid arrows indicating non-electrical processes and flow of information.
⑷, the connection line on the content of the annotation: In the system diagram and block diagram, according to the need to add various forms of comments and notes.
19, the basic characteristics of the circuit diagram and the main purpose
1, the circuit diagram: Graphic symbols and work order, the details of the circuit, equipment or complete set of all the basic composition of the connection, regardless of the actual location of the diagram.
2, legend
This circuit diagram illustrates the circuit configuration and operating principle of the compressor, M1 and fan motor M2 for power supply, control and interlocking. This diagram has the following characteristics:
⑴, According to the power supply and function divided into two parts: the main circuit according to the energy flow (ie current) flow to draw that power through the fuse, the contactor to the motor power supply; auxiliary circuit by the action sequence, that is, functional relationship drawing.
⑵, the main circuit using a vertical layout, auxiliary circuit using a horizontal layout.
⑶, the table gives the components and related technical parameters.
4, this map purposes
⑴, for the detailed expression and understanding of the design object (circuit, device or device) the role of principle, analysis and calculation of circuit characteristics.
⑵, as a basis for the preparation of wiring diagram.
(3), to provide information for testing and finding fault.












 RCCN WeChat QrCode
RCCN WeChat QrCode Mobile WebSite
Mobile WebSite